SN74HCT74 Series
High Speed CMOS Logic Dual Positive-Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flops with Set and Reset
Manufacturer: Texas Instruments
Catalog
High Speed CMOS Logic Dual Positive-Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flops with Set and Reset
Key Features
• LSTTL input logic compatibleVIL(max)= 0.8 V, VIH(min)= 2 VCMOS input logic compatibleII≤ 1 µA at VOL, VOHBuffered inputs4.5 V to 5.5 V operationWide operating temperature range: -55°C to +125°CSupports fanout up to 10 LSTTL loadsSignificant power reduction compared to LSTTL logic ICsLSTTL input logic compatibleVIL(max)= 0.8 V, VIH(min)= 2 VCMOS input logic compatibleII≤ 1 µA at VOL, VOHBuffered inputs4.5 V to 5.5 V operationWide operating temperature range: -55°C to +125°CSupports fanout up to 10 LSTTL loadsSignificant power reduction compared to LSTTL logic ICs
Description
AI
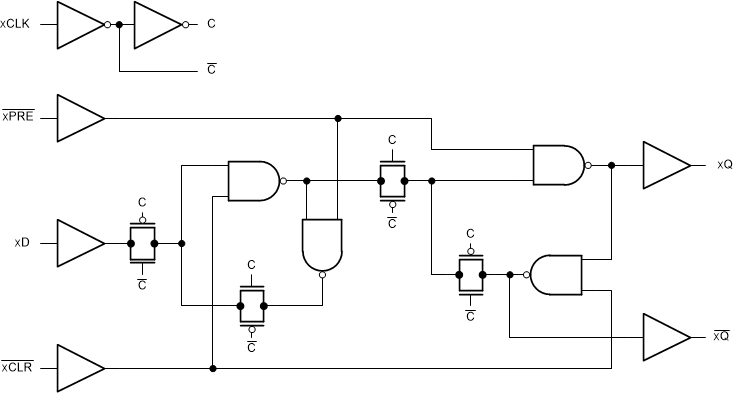
The ’HCT74 devices contain two independent D-type positive-edge-triggered flip-flops. A low level at the preset ( PRE) or clear ( CLR) inputs sets or resets the outputs, regardless of the levels of the other inputs. When PRE and CLR are inactive (high), data at the data (D) input meeting the setup time requirements are transferred to the outputs on the positive-going edge of the clock (CLK) pulse. Clock triggering occurs at a voltage level and is not directly related to the rise time of CLK. Following the hold-time interval, data at the D input may be changed without affecting the levels at the outputs.
The ’HCT74 devices contain two independent D-type positive-edge-triggered flip-flops. A low level at the preset ( PRE) or clear ( CLR) inputs sets or resets the outputs, regardless of the levels of the other inputs. When PRE and CLR are inactive (high), data at the data (D) input meeting the setup time requirements are transferred to the outputs on the positive-going edge of the clock (CLK) pulse. Clock triggering occurs at a voltage level and is not directly related to the rise time of CLK. Following the hold-time interval, data at the D input may be changed without affecting the levels at the outputs.


