SN74AHCT164-Q1 Series
Automotive, 4.5-V to 5.5-V 8-bit, parallel-out serial shift registers
Manufacturer: Texas Instruments
Catalog
Automotive, 4.5-V to 5.5-V 8-bit, parallel-out serial shift registers
Key Features
• AEC-Q100 qualified for automotive applications:Device temperature grade 1: -40°C to +125°CDevice HBM ESD classification level 2Device CDM ESD classification level C4BAvailable in wettable flank QFN packageOperating range 4.5V to 5.5V VCCTTL-Compatible inputsLow delay, 14ns max (VCC = 5V, CL = 50pF)Latch-up performance exceeds 250mAper JESD 17AEC-Q100 qualified for automotive applications:Device temperature grade 1: -40°C to +125°CDevice HBM ESD classification level 2Device CDM ESD classification level C4BAvailable in wettable flank QFN packageOperating range 4.5V to 5.5V VCCTTL-Compatible inputsLow delay, 14ns max (VCC = 5V, CL = 50pF)Latch-up performance exceeds 250mAper JESD 17
Description
AI
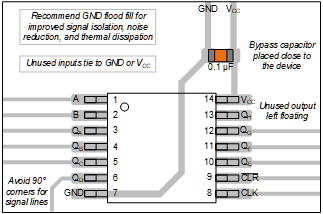
The SN74AHCT164-Q1 is an 8-bit shift register with AND-gated serial inputs and an asynchronous clear (CLR) input. Outputs are directly connected to the internal shift register, resulting in immediate output changes as values are shifted into the register. The gated serial (A and B) inputs permit complete control over incoming data; a low at either input inhibits entry of the new data and resets the first flip-flop to the low level at the next clock (CLK) pulse. A high-level input enables the other input, which then determines the state of the first flip-flop. Data at the serial inputs can be changed while CLK is high or low, provided the minimum set-up time requirements are met. Clocking occurs on the low-to-high-level transition of CLK.
The SN74AHCT164-Q1 is an 8-bit shift register with AND-gated serial inputs and an asynchronous clear (CLR) input. Outputs are directly connected to the internal shift register, resulting in immediate output changes as values are shifted into the register. The gated serial (A and B) inputs permit complete control over incoming data; a low at either input inhibits entry of the new data and resets the first flip-flop to the low level at the next clock (CLK) pulse. A high-level input enables the other input, which then determines the state of the first flip-flop. Data at the serial inputs can be changed while CLK is high or low, provided the minimum set-up time requirements are met. Clocking occurs on the low-to-high-level transition of CLK.


