ISL89411IPZ
ObsoleteHIGH SPEED, DUAL CHANNEL POWER MOSFET DRIVERS
Deep-Dive with AI
Search across all available documentation for this part.

ISL89411IPZ
ObsoleteHIGH SPEED, DUAL CHANNEL POWER MOSFET DRIVERS
Deep-Dive with AI
Technical Specifications
Parameters and characteristics for this part
| Specification | ISL89411IPZ |
|---|---|
| Channel Type | Independent |
| Current - Peak Output (Source, Sink) [custom] | 2 A |
| Current - Peak Output (Source, Sink) [custom] | 2 A |
| Driven Configuration | Low-Side |
| Gate Type | P-Channel, N-Channel |
| Input Type | Inverting |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole |
| Number of Drivers | 2 |
| Operating Temperature [Max] | 125 ¯C |
| Operating Temperature [Min] | -40 °C |
| Package / Case | 0.3 in |
| Package / Case | 8-DIP |
| Package / Case | 7.62 mm |
| Rise / Fall Time (Typ) [custom] | 10 ns |
| Rise / Fall Time (Typ) [custom] | 7.5 ns |
| Supplier Device Package | 8-PDIP |
| Voltage - Supply [Max] | 18 V |
| Voltage - Supply [Min] | 4.5 V |
Pricing
Prices provided here are for design reference only. For realtime values and availability, please visit the distributors directly
| Distributor | Package | Quantity | $ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Description
General part information
ISL89411 Series
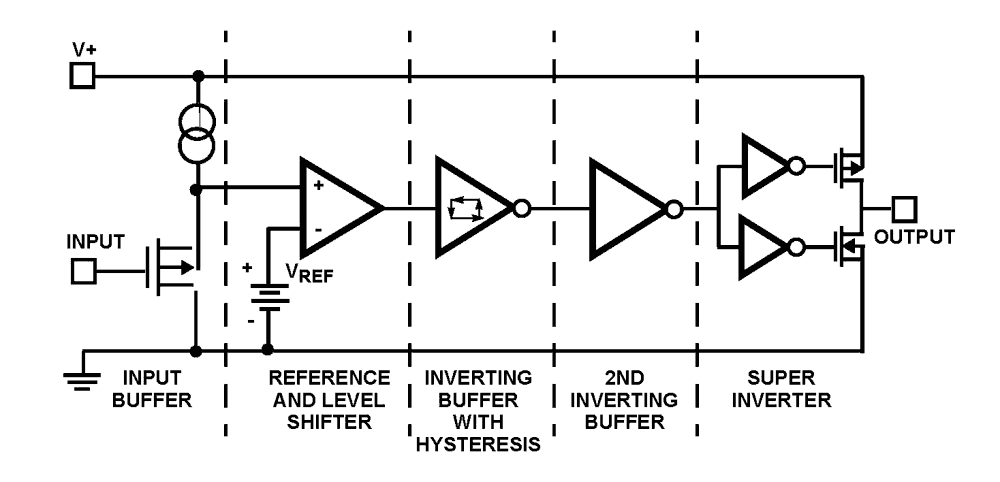
The ISL89410, ISL89411, ISL89412 ICs are similar to the EL7202, EL7212, EL7222 series but with greater VDD ratings. These are very high speed matched dual drivers capable of delivering peak currents of 2. 0A into highly capacitive loads. The high speed performance is achieved by means of a proprietary Turbo-Driver circuit that speeds up input stages by tapping the wider voltage swing at the output. Improved speed and drive capability are enhanced by matched rise and fall delay times. These matched delays maintain the integrity of input-to-output pulse-widths to reduce timing errors and clock skew problems. This improved performance is accompanied by a 10-fold reduction in supply currents over bipolar drivers, yet without the delay time problems commonly associated with CMOS devices. Dynamic switching losses are minimized with non-overlapped drive techniques.
Documents
Technical documentation and resources


