DS90CF383B Series
+3.3V LVDS Transmitter 24-Bit Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link-65 MHz
Manufacturer: Texas Instruments
Catalog
+3.3V LVDS Transmitter 24-Bit Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link-65 MHz
Key Features
• No Special Start-up Sequence Required Between Clock/Data and /PD Pins. Input Signal (Clock and Data) Can be Applied Either Before or After the Device is Powered.Support Spread Spectrum Clocking Up to 100KHz Frequency Modulation & Deviations of ±2.5% Center Spread or −5% Down Spread."Input Clock Detection" Feature Will Pull All LVDS Pairs to Logic Low when Input Clock is Missing and When /PD Pin is Logic High.18 to 68 MHz Shift Clock SupportBest–in–Class Set & Hold Times on TxINPUTsTx Power Consumption < 130 mW (typ) @65MHz Grayscale40% Less Power Dissipation Than BiCMOS AlternativesTx Power-down Mode < 60μW (typ)Supports VGA, SVGA, XGA and Dual Pixel SXGA.Narrow Cus Reduces Cable Size and CostUp to 1.8 Gbps ThroughputUp to 227 Megabytes/sec Bandwidth345 mV (typ) Swing LVDS Devices for Low EMIPLL Requires No External ComponentsCompatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS StandardLow Profile 56-Lead TSSOP PackageImproved Replacement for:SN75LVDS83, DS90CF383AAll trademarks are the property of their respective owners. TRI-STATE is a trademark of Texas Instruments. TRI-STATE is a trademark of Texas Instruments.No Special Start-up Sequence Required Between Clock/Data and /PD Pins. Input Signal (Clock and Data) Can be Applied Either Before or After the Device is Powered.Support Spread Spectrum Clocking Up to 100KHz Frequency Modulation & Deviations of ±2.5% Center Spread or −5% Down Spread."Input Clock Detection" Feature Will Pull All LVDS Pairs to Logic Low when Input Clock is Missing and When /PD Pin is Logic High.18 to 68 MHz Shift Clock SupportBest–in–Class Set & Hold Times on TxINPUTsTx Power Consumption < 130 mW (typ) @65MHz Grayscale40% Less Power Dissipation Than BiCMOS AlternativesTx Power-down Mode < 60μW (typ)Supports VGA, SVGA, XGA and Dual Pixel SXGA.Narrow Cus Reduces Cable Size and CostUp to 1.8 Gbps ThroughputUp to 227 Megabytes/sec Bandwidth345 mV (typ) Swing LVDS Devices for Low EMIPLL Requires No External ComponentsCompatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS StandardLow Profile 56-Lead TSSOP PackageImproved Replacement for:SN75LVDS83, DS90CF383AAll trademarks are the property of their respective owners. TRI-STATE is a trademark of Texas Instruments. TRI-STATE is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
Description
AI
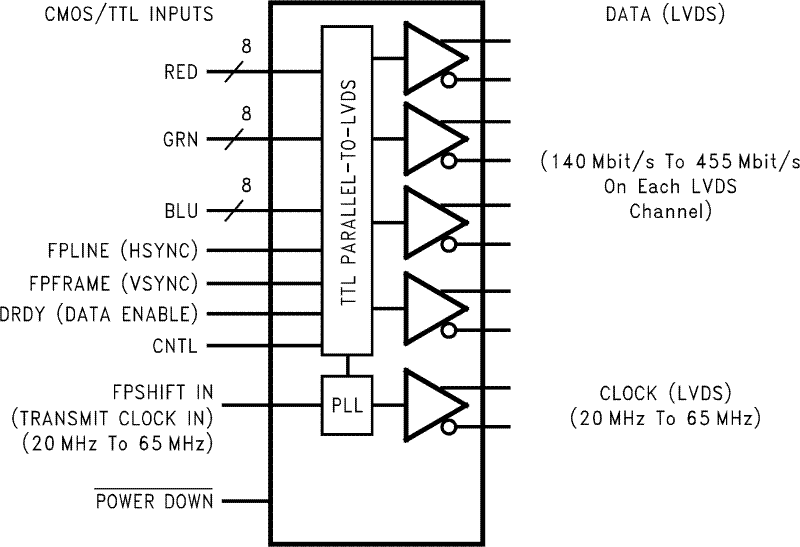
The DS90CF383B transmitter converts 28 bits of CMOS/TTL data into four LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) data streams. A phase-locked transmit clock is transmitted in parallel with the data streams over a fifth LVDS link. Every cycle of the transmit clock 28 bits of input data are sampled and transmitted. At a transmit clock frequency of 65 MHz, 24 bits of RGB data and 3 bits of LCD timing and control data (FPLINE, FPFRAME, DRDY) are transmitted at a rate of 455 Mbps per LVDS data channel. Using a 65 MHz clock, the data throughput is 227 Mbytes/sec. The DS90CF383B is fixed as a Falling edge strobe transmitter and will interoperate with a Falling edge strobe Receiver (DS90CF386) without any translation logic.
This chipset is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high speed TTL interfaces.
The DS90CF383B transmitter converts 28 bits of CMOS/TTL data into four LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) data streams. A phase-locked transmit clock is transmitted in parallel with the data streams over a fifth LVDS link. Every cycle of the transmit clock 28 bits of input data are sampled and transmitted. At a transmit clock frequency of 65 MHz, 24 bits of RGB data and 3 bits of LCD timing and control data (FPLINE, FPFRAME, DRDY) are transmitted at a rate of 455 Mbps per LVDS data channel. Using a 65 MHz clock, the data throughput is 227 Mbytes/sec. The DS90CF383B is fixed as a Falling edge strobe transmitter and will interoperate with a Falling edge strobe Receiver (DS90CF386) without any translation logic.
This chipset is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high speed TTL interfaces.


