DS90CR218A Series
+3.3V Rising Edge Data Strobe LVDS 21-Bit Channel Link Receiver - 85 MHz
Manufacturer: Texas Instruments
Catalog
+3.3V Rising Edge Data Strobe LVDS 21-Bit Channel Link Receiver - 85 MHz
Key Features
• 12 to 85 MHz Shift Clock Support50% Duty Cycle on Receiver Output ClockLow Power Consumption±1V Common-mode Range (Around +1.2V)Narrow Bus Reduces Cable Size and CostUp to 1.785 Gbps ThroughputUp to 223 Mbytes/sec Bandwidth345 mV (typ) Swing LVDS Devices for Low EMIPLL Requires No External ComponentsRising Edge Data StrobeCompatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS StandardLow Profile 48-Lead TSSOP PackageAll trademarks are the property of their respective owners.12 to 85 MHz Shift Clock Support50% Duty Cycle on Receiver Output ClockLow Power Consumption±1V Common-mode Range (Around +1.2V)Narrow Bus Reduces Cable Size and CostUp to 1.785 Gbps ThroughputUp to 223 Mbytes/sec Bandwidth345 mV (typ) Swing LVDS Devices for Low EMIPLL Requires No External ComponentsRising Edge Data StrobeCompatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS StandardLow Profile 48-Lead TSSOP PackageAll trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Description
AI
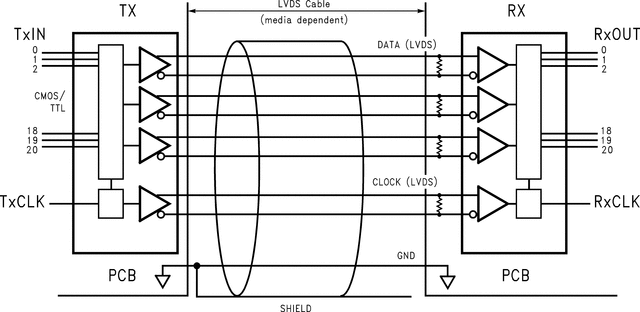
The DS90CR218A receiver deserializes three input LVDS data streams into 21 bits of CMOS/TTL output data. When operating at the maximum input clock rate of 85 Mhz, the LVDS data is received at 595 Mbps per data channel for a total data throughput of 1.785 Gbit/sec (233 Mbytes/sec).
The narrow bus and LVDS signalling of the DS90CR218A is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high-speed TTL interfaces.
The DS90CR218A receiver deserializes three input LVDS data streams into 21 bits of CMOS/TTL output data. When operating at the maximum input clock rate of 85 Mhz, the LVDS data is received at 595 Mbps per data channel for a total data throughput of 1.785 Gbit/sec (233 Mbytes/sec).
The narrow bus and LVDS signalling of the DS90CR218A is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high-speed TTL interfaces.


