SN65HVD1787 Series
30-V Fault-Protected RS-485 with -20 to +25 common mode
Manufacturer: Texas Instruments
Catalog
30-V Fault-Protected RS-485 with -20 to +25 common mode
Key Features
• Bus-Pin Fault Protection to:> ±70 V (’HVD1785, 86, 91, 92)> ±30 V (’HVD1787, 93)Common-Mode Voltage Range (–20 V to 25 V) More Than Doubles TIA/EIA 485 RequirementBus I/O Protection±16 kV JEDEC HBM ProtectionReduced Unit Load for Up to 256 NodesFailsafe Receiver for Open-Circuit, Short-Circuit and Idle-Bus ConditionsLow Power ConsumptionLow Standby Supply Current, 1 µA TypicalICC5 mA Quiescent During OperationPower-Up, Power-Down Glitch-Free OperationBus-Pin Fault Protection to:> ±70 V (’HVD1785, 86, 91, 92)> ±30 V (’HVD1787, 93)Common-Mode Voltage Range (–20 V to 25 V) More Than Doubles TIA/EIA 485 RequirementBus I/O Protection±16 kV JEDEC HBM ProtectionReduced Unit Load for Up to 256 NodesFailsafe Receiver for Open-Circuit, Short-Circuit and Idle-Bus ConditionsLow Power ConsumptionLow Standby Supply Current, 1 µA TypicalICC5 mA Quiescent During OperationPower-Up, Power-Down Glitch-Free Operation
Description
AI
These devices are designed to survive overvoltage faults such as direct shorts to power supplies, mis-wiring faults, connector failures, cable crushes, and tool mis-applications. They are also robust to ESD events, with high levels of protection to human-body model specifications.
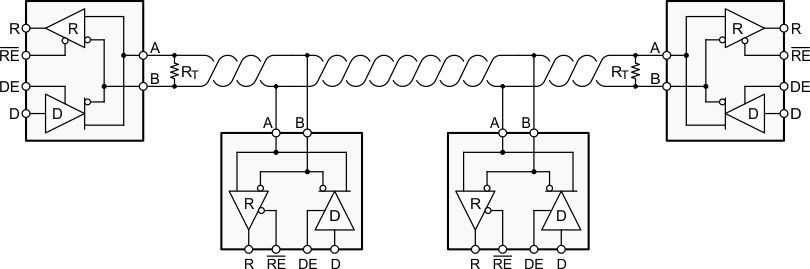
These devices combine a differential driver and a differential receiver, which operate from a single power supply. In the ’HVD1785, ’HVD1786, and ’HVD1787, the driver differential outputs and the receiver differential inputs are connected internally to form a bus port suitable for half-duplex (two-wire bus) communication. In the ’HVD1793, the driver differential outputs and the receiver differential inputs are separate pins, to form a bus port suitable for full-duplex (four-wire bus) communication. These ports feature a wide common-mode voltage range, making the devices suitable for multipoint applications over long cable runs. These devices are characterized from –40°C to 105°C.
For similar features with 3.3-V supply operation, see the SN65HVD1781 (SLLS877).
These devices are designed to survive overvoltage faults such as direct shorts to power supplies, mis-wiring faults, connector failures, cable crushes, and tool mis-applications. They are also robust to ESD events, with high levels of protection to human-body model specifications.
These devices combine a differential driver and a differential receiver, which operate from a single power supply. In the ’HVD1785, ’HVD1786, and ’HVD1787, the driver differential outputs and the receiver differential inputs are connected internally to form a bus port suitable for half-duplex (two-wire bus) communication. In the ’HVD1793, the driver differential outputs and the receiver differential inputs are separate pins, to form a bus port suitable for full-duplex (four-wire bus) communication. These ports feature a wide common-mode voltage range, making the devices suitable for multipoint applications over long cable runs. These devices are characterized from –40°C to 105°C.
For similar features with 3.3-V supply operation, see the SN65HVD1781 (SLLS877).


